
Muscles of the palate are shown tensor veli palatini (TVP), levator... Download Scientific Diagram
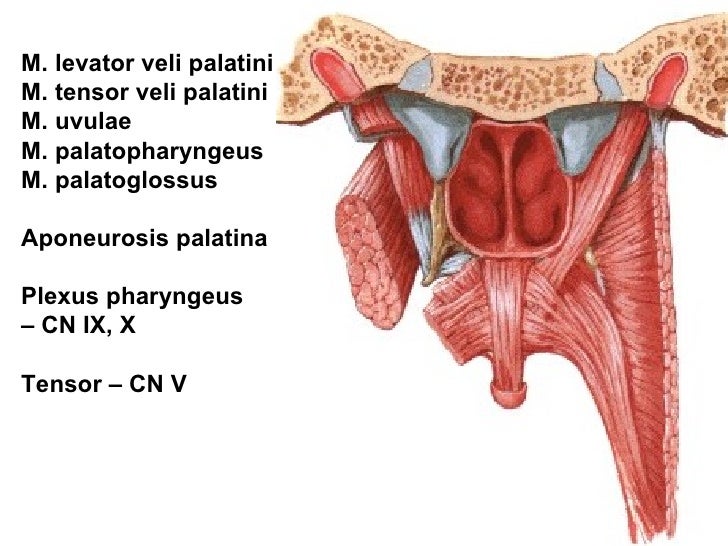
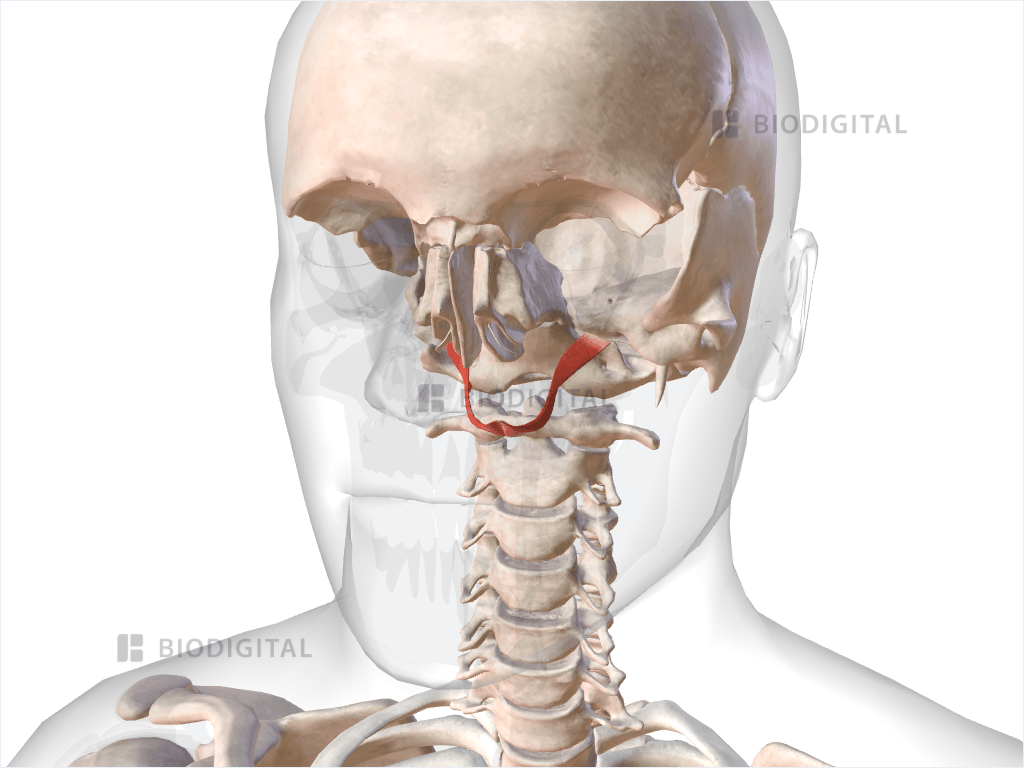
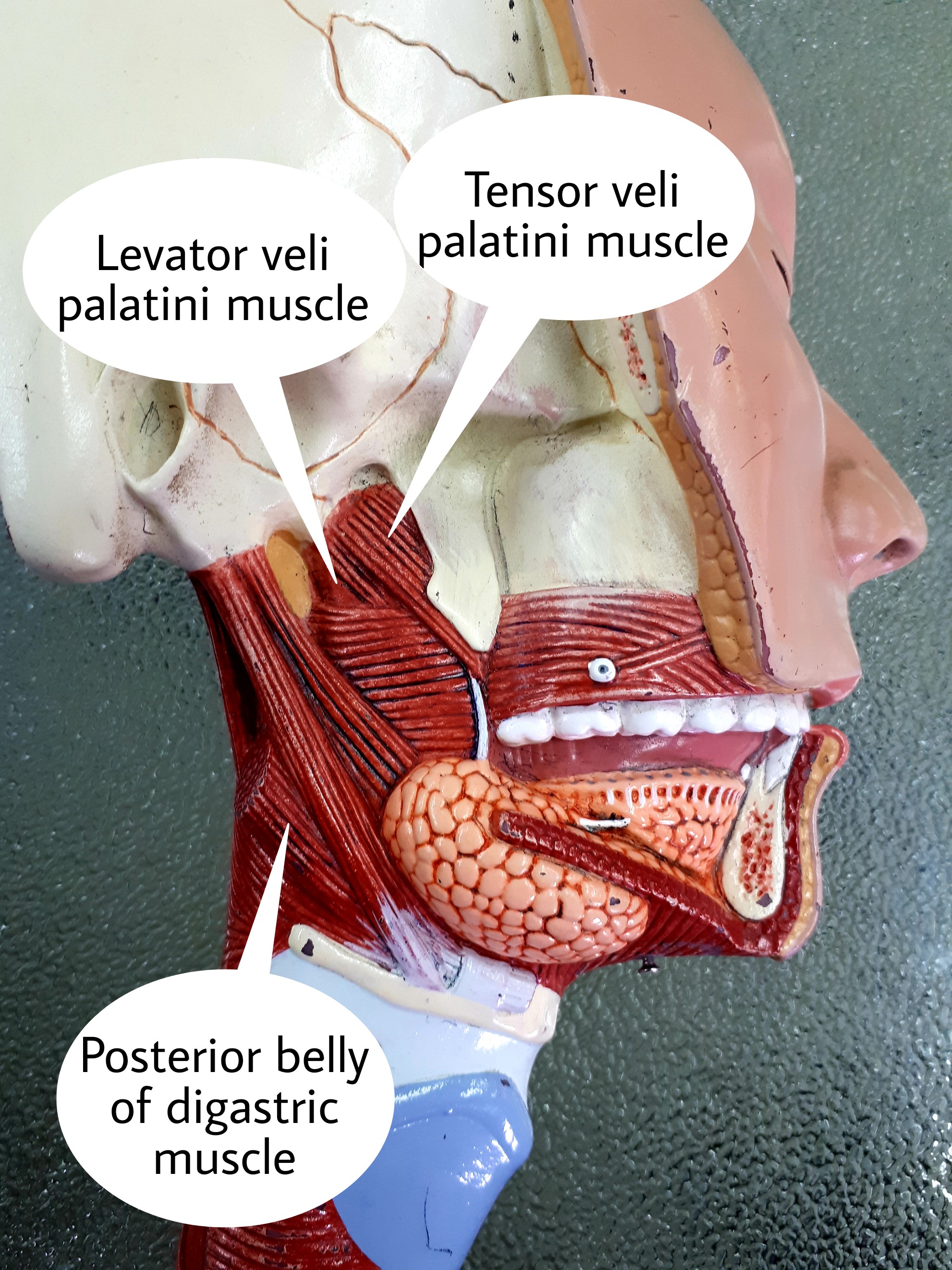
Levator veli palatini is a paired cylindrical muscle situated lateral to the choanae of nasal cavity, spanning from the petrous part of temporal bone to the superior part of palatine aponeurosis. Together with tensor veli palatini, palatoglossus, palatopharyngeus muscles and musculus uvulae, levator veli palatini comprises the soft palate .
1st week _digestive_system_i
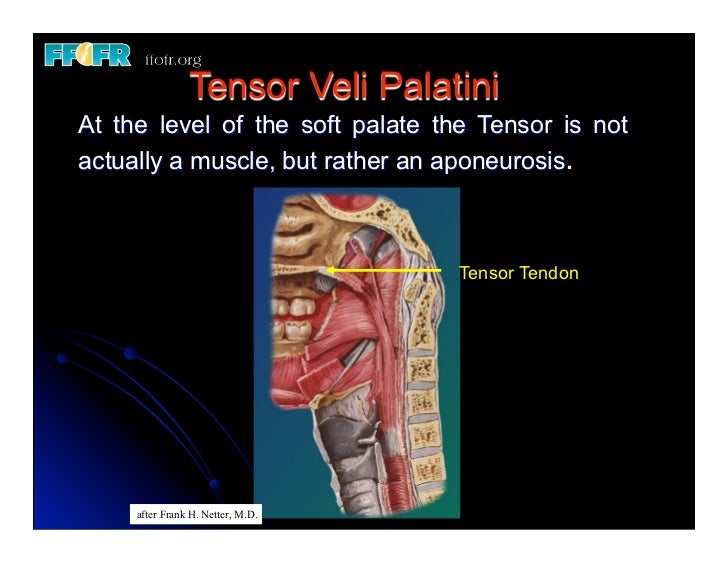
Tensor veli palatini Latin synonym: Musculus tensor veli palatini Synonym: Tensor veli palatini muscle Definition Origin: Medial pterygoid plate of the sphenoid bone Insertion: Palatine aponeurosis Nerve: Medial pterygoid of mandibular nerve
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/article/en/tensor-veli-palatini-muscle/skxO2GDICmPjAlVEnkfgUA_Tensor_veli_palatini_muscle.png)
Tensor veli palatini Origin, insertion and function Kenhub
This study aimed to perform a thorough review of the literature on (1) the role of the tensor veli palatini muscle in the Eustachian tube opening and middle ear ventilation, (2) anatomical anomalies in cleft palate infants related to middle ear disease, and (3) their implications for surgical techniques used in cleft palate repair.

Tensor Veli Palatini Origin And Insertion
While carrying out the repair, some surgeons prefer to cut the tensor veli palatini (TVP) tendon, others perform a tenopexy or fracture the hamulus around which the tendon passes, to.

Muscles of soft palateTensor veli palatini YouTube
The tensor veli palatini muscle ( tensor palati or tensor muscle of the velum palatinum) is a thin, triangular muscle of the head that tenses the soft palate and opens the Eustachian tube to equalise pressure in the middle ear. Structure The tensor veli palatini muscle is thin and triangular in shape. [1] Origin
Levator veli palatini BioDigital Anatomy
This study aimed to perform a thorough review of the lit-erature on (1) the role of the tensor veli palatini muscle in the Eustachian tube opening and middle ear ventilation, (2) ana-tomical anomalies in cleft palate infants related to middle ear disease, and (3) their implications for surgical techniques used in cleft palate repair.
19.(new)speech and velopharyngeal function
The tensor veli palatini muscle originates from the bony wall of the scaphoid fossa and from the entire length of the short lateral lamina of the cartilage tube, to descend converging into a short tendon that turns medially around the pterygoid hamulus. It then fans out within the soft palate and mingles with the fibers from the opposite side.
عضله بالابرنده کام نرم اطلس الکترونیک آناتومی
The tensor veli palatini contracts the anterolateral wall to cause dilation and opening of the distal Eustachian tube. Contraction of the levator veli palatini results in elevation of the soft palate and medial rotation of the cartilaginous lamina. Simultaneous contractions of these muscles during swallowing or yawning allow air to pass through.

tensor veli palitini YouTube
Embryology The tensor veli palatini begins to develop as early as 6 weeks into gestation. It originates from the first pharyngeal arch's mesenchyme, specifically from the medial blastema. [5] [8] Because the TVP is near the pharyngotympanic tube, it is considered a paratubal or peritubal muscle.

M. tensor veli palatini
The tensor veli palatini muscle is one of the five paired muscles of the soft palate. It is triangular in shape and its tendon wraps around the pulley of pterygoid hamulus to alter the shape of the soft palate. Summary origin: it has three sites of origin: scaphoid fossa of the medial pterygoid plate medial aspect of spine of sphenoid bone

Muscles of Pharynx Lateral View Anatomy Pharyngobasilar fascia , Tensor veli palatini muscle
Tensor veli palatini Quick Facts Origin Insertion Key Features & Anatomical Relations Actions References Quick Facts Origin: Scaphoid fossa and spine sphenoid bone and wall of auditory tube. Insertion: Palatine aponeurosis. Action: Opens auditory tube; tenses soft palate. Innervation: Nerve to tensor veli palatini (CN V3).

Tensor Veli Palatini Origin And Insertion
NLM NIH HHS USA.gov Tinnitus is the perception of sound that does not originate from a source external to the individual's body. When discussing tinnitus, it is first crucial to categorize it between either subjective or objective, as well as between pulsatile and non-pulsatile tinnitus.

11 Botulinum Neurotoxin for Palatal Myoclonus Neupsy Key
The levator veli palatini ( / lɪˈveɪtər ˈviːlaɪ ˌpæləˈtaɪnaɪ /) is a muscle of the soft palate and pharynx. It is innervated by the vagus nerve (cranial nerve X) via its pharyngeal plexus. During swallowing, it contracts, elevating the soft palate to help prevent food from entering the nasopharynx . Structure

Hypothetical reconstruction of tensor veli palatini muscle and tendon... Download Scientific
Abstract Purpose: To investigate the dimensions of the tensor veli palatini (TVP) muscle using high image resolution 3D MRI of the soft palate among children with normal velopharyngeal and craniofacial anatomy and to compare values to individuals with a diagnosis of 22q11.2 deletion syndrome (22q11DS).
:watermark(/images/logo_url.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/anatomy_term/pharyngeal-opening-of-auditory-tube/THNkIPEI0KRJ666rY21Fw_Ostium_pharyngeum_tubae_auditivae_02.png)
Tensor veli palatini Origin, insertion and function Kenhub
The anatomic relationships among the levator veli palatini muscle (LVPM), the tensor veli palatini muscle (TVPM), and the eustachian tube (ET) cartilage were investigated by computer-aided 3-dimensional reconstruction and measurement methods.

Origin of the Mammalian Fauces Crompton Lab
The aim of the study is to analyze the function of the tensor veli palatini (TVP) muscle electromyographically in chronic middle ear pathologies and to evaluate the role of this muscle in eustachian tube dysfunction and pathogenesis of associated middle ear diseases by comparing with the results of healthy individuals. Study design: A.